Lead is a widely used heavy metal since it was discovered centuries ago. But is lead a safe metal? Are lead-based products toxic or hazardous?
The truth is, lead as a solid metal is almost non-reactive to fire, so it is not flammable and does not catch fire. On the other hand, lead dust is combustible and may cause an explosion.
Lead and lead-based products carry significant body and environmental hazards. Lead poisoning can affect children’s growth and development. Adults also suffer from lead poisoning, which may even result in death.
This post contains affiliate links. I may earn a small commission at NO extra cost to you for purchases made through these links. Disclosure.
What is Lead?
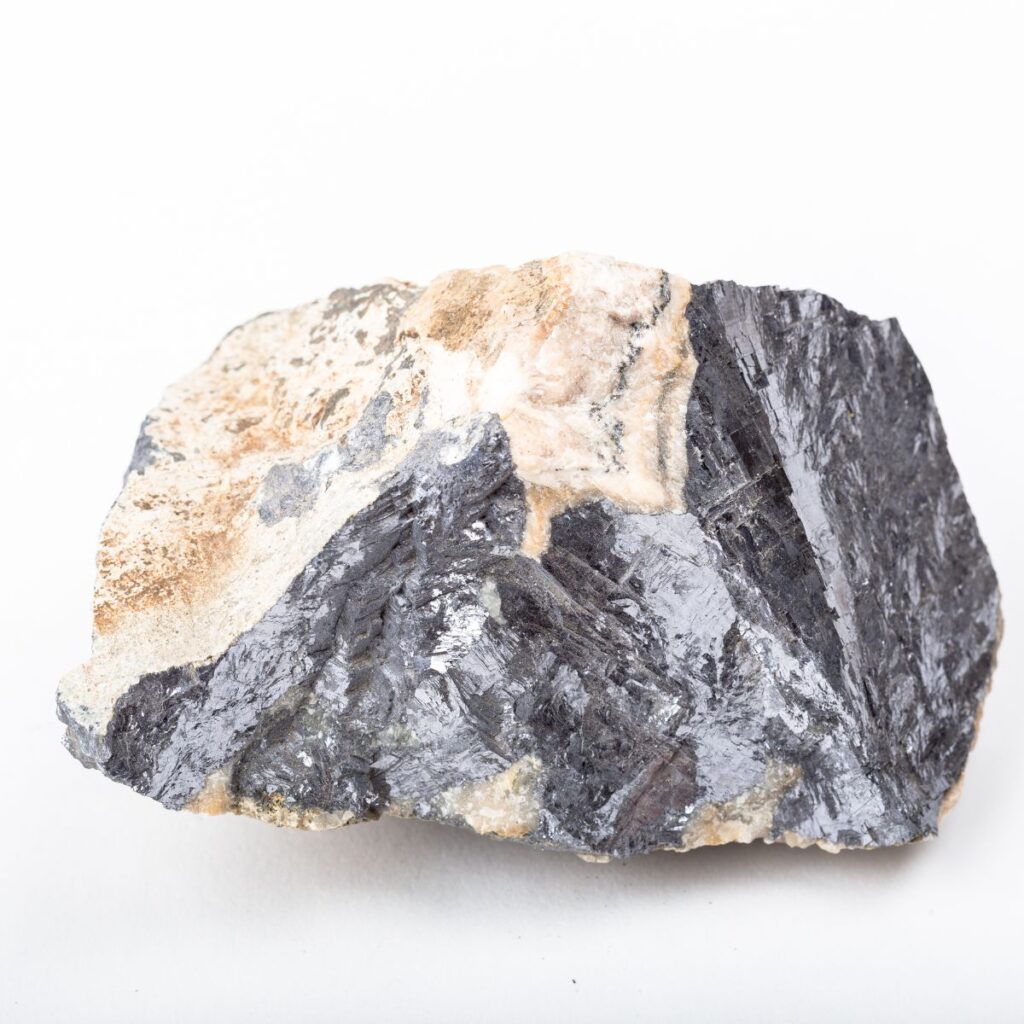

Lead is a heavy metal discovered and used since ancient times. It is heavy yet soft and is uniquely characterized by its blue-gray coloring.
Lead was one of the earliest metals utilized by humans. According to records, Lead was first used to line baths and seal water pipes. Later, Lead was used in roofs, tanks, and gutters, among other things.
Numerous cultures also utilized Lead to produce decorative products, such as statues and pottery.
Modern Applications of Lead
Lead is super malleable, soft, and dense, and all these properties make Lead an excellent metal to work with. According to the International Lead Association, Lead is a highly useful metal used across numerous industries. Its main applications include:
- Production of batteries (including batteries for electric vehicles and emergency power supply)
- Soldering
- Plumbing
- Radiation shielding
- Paints
- Combustion engine
- Ammunition
- Weights
- and so much more!

Related Posts
- Understanding the Different Classes of Fire and How to Extinguish Them
- Is Powdered Creamer Flammable?
- Is Fiberglass Insulation Flammable? Facts You Need to Know
- Is Magnesium Flammable?
- Should You Boil or Not Boil Fabuloso?
- Is Freon Flammable? Does It Explode?
Is Lead Flammable? Does It Catch Fire?
One of the most interesting things about Lead compared to other metals is how it reacts with oxygen. Apparently, Lead is non-reactive to oxygen, which means it isn’t flammable.
Also, Lead has a high melting point of 621.5 F and a boiling point of 3100 degrees F. This means that Lead is highly tolerant and does not react so much to high heat.
Lead Burning
While we consider lead a non-flammable metal, it can also burn, given the right circumstances.
A process called lead burning presents this kind of circumstance. Lead burning happens when you use high heat to join two sheets through the process of welding. It is carried out with gas welding equipment, a torch, and a rod.
Before, lead welding was a common process among plumbers. But given the toxic nature of Lead, this practice has become obsolete. Still, lead welding is used by many roofers.
What Happens If You Put Lead on Fire?
Now we know that Lead does not burn, but objects that contain Lead do burn. For instance, older homes or buildings built before the 1970s probably used lead-based paint.
If such a structure burns catches fire, so does lead. When the temperature reaches 932 degrees F or more, fumes from Lead are released into the air in the form of lead oxide. Lead oxide may remain floating in the air or become soot or ash. Either way, you could get sick when exposed to lead fumes through inhalation or ingestion.
Is It Bad to Burn Lead?

Yes, burning Lead is bad. Although Lead is generally non-reactive to fire, the by-products from heating lead through the process of welding, for example, is a health hazard.
You can be exposed to lead through these methods: skin contact, inhalation, and ingestion. When this happens, you can get sick of “lead poisoning.” Let’s discuss the details of this disease below.
The Health Hazards of Lead
According to the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), you can get lead poisoning by breathing in, swallowing, or skin contact with Lead.
Whichever the manner of exposure, your body faces irreversible damage when exposed to Lead.
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health says that exposure to lead can cause severe disease and affect the health of adults and children.
This disease is called lead poisoning, which is caused by exposure to high levels of Lead over a short period. When you are exposed to lead, you experience the following symptoms:
- Weakness
- Abdominal pain
- Headaches and tiredness
- Irritability
- Memory loss
- Constipation
- Loss of appetite
Effects of Lead Poisoning
These symptoms occur over time, so most people dismiss them without getting checked. But lead exposure that goes untreated can result in blood, brain, and kidney damage, anemia, and even death. Lead is also suspected to be a cancer hazard and may cause infertility and genetic defects.
Pregnant women may also pass this disease to their unborn children. Lead exposure can damage their nervous system, affecting their cognitive and behavioral development.
The health impacts of lead poisoning are worse in kids than in adults. Also, NIOSH pointed out that kids may become susceptible to lead poisoning when parents bring home lead dust through their clothing or if such parents are workers in a lead-related industry.
With that said, it is important for workers to get tested regularly for lead exposure in the workplace. Since Lead can penetrate our body through ingestion, inhalation, and skin contact, exposure can’t be helped even when one is wearing protection (such as masks and goggles).
Where Can You Find Lead?
It might surprise you, but lead exposure is more common than we realize. According to World Health Organization, lead poisoning accounts for 21.7% of deaths and disabilities worldwide.
But where can you find Lead? According to the Agency of Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, Lead can be found in a lot of places, particularly:
- Older homes and buildings that used lead-based paint
- Drinking water where water pipes had been soldered with Lead
- Workplaces where Lead is handled
- In some children’s toys, cosmetics, and other commercial products
- Lead seep into the soil, water, or air where there is mining or smelting
According to WHO, there are a couple of exposure methods that result in lead poisoning. For instance, a burning old building with lead-based paint emits toxic lead fumes into the air.
Additionally, ingestion of food contaminated with lead dust and consumption of water coming from lead-soldered pipes can prove to be risky.
Lead poses five more times the hazards to children. That is because they are more curious and they are prone to hand-to-mouth behavior. Sometimes they don’t know that they are ingesting something so poisonous!
Workers at lead-based businesses are not only overexposed to lead, but they might carry Lead from their workplace and into their homes.
Improper disposal and recycling of lead batteries have also been associated with multiple deaths of kids in Africa.
How to Prevent Lead Poisoning?
Lead poisoning is a real health risk that can cause disability and death. For your own safety and protection, here are the best ways to prevent lead poisoning:
- Relocate your family. If you reside in an older house, chances are, it still has lead-based paint. The best way to protect young children from exposure is to move to a newer building.
- Practice regular hand-washing. Kids of young age tend to put things into their mouths, and those could be lead-contaminated. Regular handwashing can wash away the lead dust away from their hands.
- Do not wear your shoes inside your house. Shoes worn outside may have picked up lead dust from the streets or soil.
- Always clean your home to prevent the build-up of dust.
- Take your vitamins. Taking Vitamins C and D can help lower the absorption rate of Lead into the body. Also, eating a well-balanced diet help build up immunity.
Is Lead Dust Combustible?
Although Lead as a solid metal does not burn or catch fire, lead, in its dust form, is also a health and safety hazard.
Lead dust is combustible. And like other combustible dusts, Lead particles can form into a dust cloud which can cause a severe explosion.
Do Lead Acid Batteries Catch Fire? Do They Explode?
One of the most essential applications of Lead is in the battery industry. Lead acid batteries were popular before lithium-ion batteries entered the picture.
That is due in part to the risks related to lead acid batteries. While charging, a lead acid battery delivers a powerful electric charge and releases hydrogen and oxygen. Hydrogen is flammable while oxygen reinforces combustion — a recipe for an explosion!
Apart from lead acid battery exploding, the electrolyte or the chemical contained in the batteries is also corrosive. Workers must handle electrolytes carefully for their own safety. Contact with electrolytes may cause eye damage and chemical burns to the skin. The spilled electrolyte may also cause damage to property and the environment.
Conclusion
Lead is a very useful metal. But we can’t also ignore the fact that dealing with Lead and exposure to it can be risky business. Lead poisoning can enter the blood, attack the nervous system, severely damage the kidneys and even cause death.
So if you suspect you are in contact with Lead (or just want to play it safe for your family), follow the measures mentioned above and seek medical help immediately.


Leave a Reply